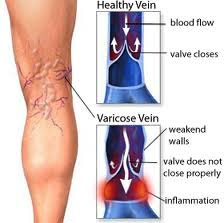
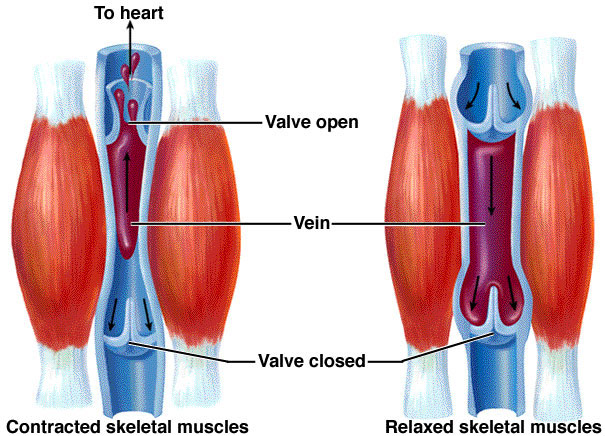
Veins are blood vessels that return deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body back to the heart. When veins become abnormally thick, full of twists and turns, or enlarged, they are called varicose veins. This happens most commonly in the veins in the legs and thighs.
- The thickened, twisting or dilated parts of the vein are called varicosities.
- Varicose veins can form anywhere in the body, but they are most often located in the legs.
- Varicose veins tend to be inherited, and become more prominent as a person ages.
Veins in the leg are either superficial or deep.
- The superficial veins and their branches are close to the skin. The communicator or perforator veins connect the superficial veins with the deep veins.
- The deep veins are covered by muscle and connective tissue, which help to pump the blood in the veins and back to the heart. The veins have one-way valves to prevent back flow of blood.
Generally, blood travels from the superficial veins to the deep veins. From there, the blood travels through a network of larger veins back to the heart.
Varicose Vein Causes
Any condition that puts excessive pressure on the veins makes them dilated and twisted. They commonly affect the legs and feet although they can appear anywhere. Haemorrhoids are also varicose veins. Some causes of varicose veins are
- Occupation involving prolonged standing
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Tight clothing
- Chronic Tumours in abdomen
- Excessive physical activity that puts pressure on the legs
- Ageing leads to loss of skin elasticity as well as thinning of veins
- Dietary deficiencies
- Pregnancy.
- Obesityor distended belly
- Straining : Chronic constipation, urinary retentionfrom an enlarged prostate, chronic cough
- Age: most elderly individualsshow some degree of varicose vein occurrence.
Varicose Vein Symptoms
Varicose veins are relatively easy to identify and can be a cosmetic nuisance for many people.
- They protrude or bulge from under the skin and feel ropey
- The legs often ache and feel heavy and itchy
- Symptoms can intensify after a long day of standing the feet
- A person may have severe pain upon standing or even have cramps in the legs at night.
Varicose veins are prone to developing superficial thrombophlebitis, which is a blood clot along with inflammation of
a segment of vein.
When to Seek Medical Care
If a person has varicose veins, any of the following warrant a visit to a health care professional:
- redness, discoloration, or ulceration of the skin
- swelling of the calf or leg
Varicose Veins Diagnosis
- Doppler ultrasound – A specialized sonography
- Magnetic resonance venography - This test can even look for blood clots in the deep veins.
Varicose Veins Self-Care at Home
- Regular exercise to keep leg muscles toned and to improve blood circulation. Walking is good exercise which
help the muscles force the blood out of the deeper vein system.
- Control over weight
- Diet should be low in fat, sugar and salt but rich in proteins. Include fresh fruits like amla & other
citrus fruits in diet.
- Drink plenty of water
- Quit smoking as it leads to increased blood pressure and this worsens varicose veins
- Wear support stockings
- Foot elevation while sitting or resting for long periods of time
- Vitamin E oil application is advisable.
- Stop contraceptive pills
- If pregnant, sleep on left side rather than back
- Avoid alcohol, which can cause the veins in the legs to dilate.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing such as girdles or belts.
- Do not cross the legs when sitting.
- Any task which require sitting for long time, try to get up and walk around every hour to allow the muscles to
pump blood out of the veins.
Varicose Veins Medical Treatment
Sclerotherapy
involves injecting a chemical inside the vein that obliterates it and causes it to collapse.
Lasers
Lasers are also used as a treatment for varicose veins, but are frequently used in the treatment of smaller veins, medically referred to as telangiectasias.
Varicose Veins Surgery
- The surgery involves either vein ligation (tying) or stripping or avulsion (pulling away) of the smaller branches.
1)Avulsion - Avulsion requires many tiny incisions and removal of the varicose veins that have been outlined on the skin.
2)Stripping - here the entire vein is stripped off
3)Endovascular laser therapy -Endovenous laser therapy is a technique that uses a laser to destroy the vein
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a similar technique to endovascular laser, but it uses heat to destroy the vein.
Litigation
It usually involved an incision at the groin and tying off of the saphenous vein where it enters the femoral vein.
Varicose Veins Prevention
- to develop varicose veins, they may appear despite all the best efforts.
- Pressure stockings are the best nonsurgical treatment of varicose veins. They prevent skin breakdown and worsening of the varicosities.
Varicose Veins Prognosis
Prevention is the key. The earlier a person starts the lifestyle modifications the better the chances of preventing new varicose veins from forming.
Some people may progress from having no symptoms, to the development of varicose veins, and then on to problems with leg swelling, and finally to ulcers caused by stagnant blood flow.
- A small number of these people will have deep vein clots as a cause for their signs and symptoms, but most will not.
- The more severe problems, such as skin ulcers, tend to be very difficult to prevent completely. Once these ulcers occur, they are very difficult to cure.
- Even when they are eliminated, these ulcers tend to recur
A deep vein blood clot has the potential to travel through the bloodstream and lodge in the lung. This is called a pulmonary embolism or to the brain causing paralysis or to the heart causing heart attack.